Abstract IMAFS the inventory optimization software helps knowledge gathering areas, such as, solution oriented and stock availability management, best practices in inventory management, support from experts, evolution of ROI before implementation and simplify integration, proven and rigorous implementation methodology using cloud/SAAS mode, continuous improvement with R&D, and user-friendly, integration manual parameters also. A poor delivery performance can affect consumption history.A […]
Author: ikram
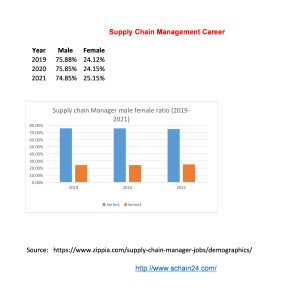
What is a Supply Chain Management Job and Career?
Abstract In a case study, based on US-based companies, first-level management is of about 0-4 years. To understand the supply chain management job and career we can remind ourselves about the example of leaf cutter ants. APICS, founded in 1957 as American Production and Inventory Control Society and re-branded as The Association for Supply Chain Management in 2018, launched their […]
What is drop shipping: a supply chain distribution network option |
In drop-sip model, product is shipped directly from manufacturer end bypassing a retailer. Benefits of aggregation can be achieved, if the manufacturer can keep some of its inventory at the retailer end on and as needed basis. In addition, drop-shipping offers manufacturer an opportunity to postpone customization until the customer has placed order finally. Response times tend to be long, because the order has to be transmitted from retailer to the manufacturer and shipping distance are generally longer from the manufacturer’s centralizing site. Order visibility is very important in the context of manufacturer storage, because two stages in the supply chain are involved in every customer order. But a manufacturer storage network is likely to have difficulty handling returns, so that customer satisfaction may be hurt. Because, each order may involve more than one manufacturer.
Keywords: drop-shipping.
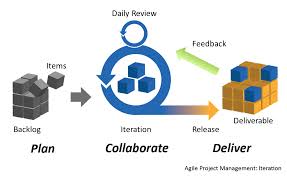
How to be a supply chain manager and what are the roles?
Abstract Supply chain managers are crucial in connecting different parts of a business’s supply chain, ensuring the value of the supply chain increases through effective management of supplier support, transportation, and distribution practices. They manage manufacturing and distribution processes, work with procurement managers, buyers, and vendors, negotiate contracts, use software to track goods, use data analytics to forecast demand, cut […]
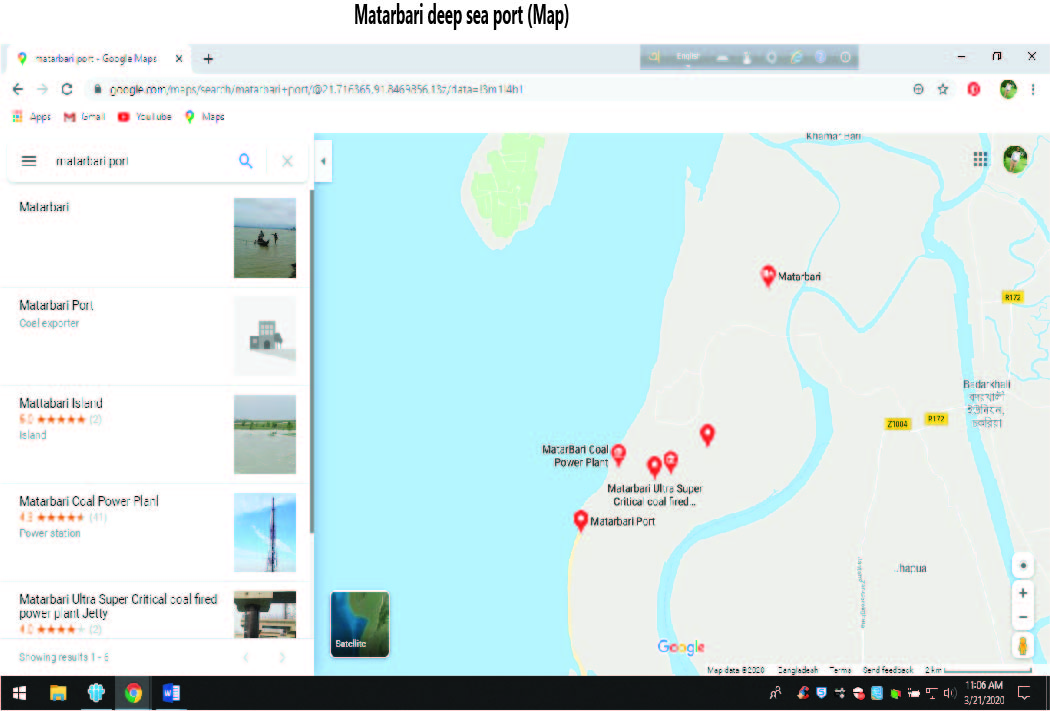
About the Matarbari deep sea port: An SCM perspective
To ensure load unload of deep draft vessels the Matarbari port is essential for Bangladesh and adjacent countries and areas. The Matarbari deep sea port has a 16m depth that will help 16m draft vessels to unload their cargo at the terminal. At deep sea, currently mother vessels unload the cargo at feeder vessel and they carry the cargo to the Chittagong port. The present seaports (Chattogram sea port and Mongla sea port) of the country do not have the capacity to handle huge containers and vessels and the building of a deep sea port is the only solution. Chittagong port can’t load unload from more than 9.5 meter vessels.
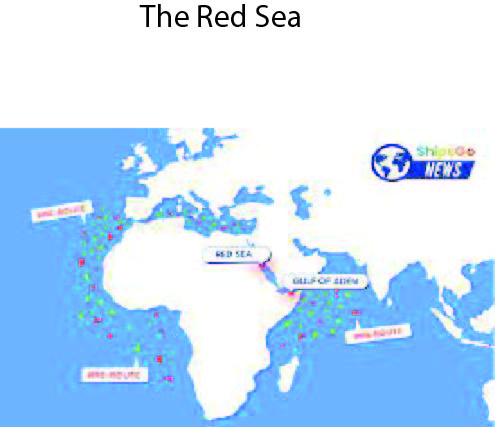
The Red Sea: A discussion in a supply chain perspective
The Red Sea, a major sea route connecting Europe, the Persian Gulf, and East Asia, is facing increased attacks by Houthi insurgents in Yemen since mid-November 2023. The US has announced a maritime coalition to defend shipping in the area. The Eastern shore includes Saudi Arabia and Yemen, while the Western shore includes Egypt, Sudan, Eritrea, and Djibouti. Maersk has halted all transits through the Red Sea/Gulf of Aden until further notice, while Hapag-Lloyd has extended its rerouting around Africa. CMA CGM has announced rate increases from Asia to North Europe, and carriers are redirecting Asia to US East Coast services via Panama.
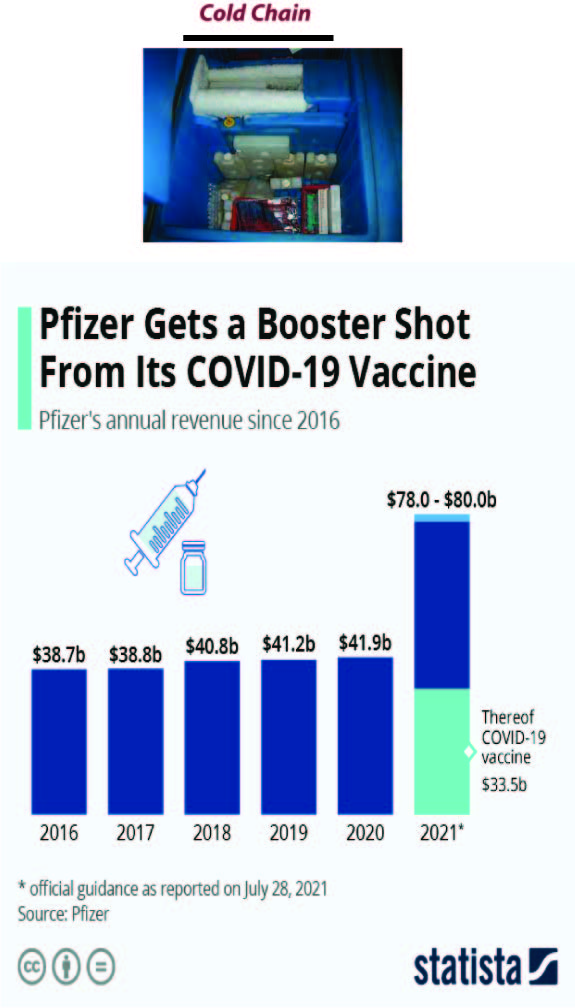
Cold chain: A cutting-edge SCM and logistics perspective
Existing amenities not enough to store, deliver large volume of vaccines within a short time, say experts The governments are considering banking on the existing cold chain for storing, transporting and distributing coronavirus vaccines while some professionals say the main challenge will be to manage such a large volume with the existing capacity. On November 5,2020 the Bangladesh government signed a trilateral memorandum of understanding (MoU) with Serum Institute of India and Bangladesh’s Beximco Pharmaceuticals Ltd to get three crore doses of Covid-19 vaccines from Serum, keeping in mind the existing cold chain. In 2020 during the COVID-19 pandemic, vaccines being developed may need ultra-cold storage and transportation temperatures as cold as −70 °C (−94 °F), requiring what has been referred to as a “colder chain” infrastructure. Disruption of a cold chain due to war may produce consequences similar to the smallpox outbreaks in the Philippines during the Spanish–American War, during which the distributed vaccines were inert due to lack of temperature control in transport. There are no uniform global practices to follow, customs, legal, and compliance issues, effects on the environment, supplier-related risks, issues with cold chain delivery — packaging, hardware issues, vehicle breakdown, etc. Besides the usual elements of risk that plague normal supply chains, cold chain logistics has its own exclusive set of problems such as product sensitivity, the increasing cost of freight, and growing regulatory hurdles.
Keywords: Cold Chain, Supply chain management, Vaccines, food.