Featured Posts
View AllUnveiling Amazon’s Digital Supply Chain Strategies: A Case Study
- ikram
- April 10, 2025
- 0
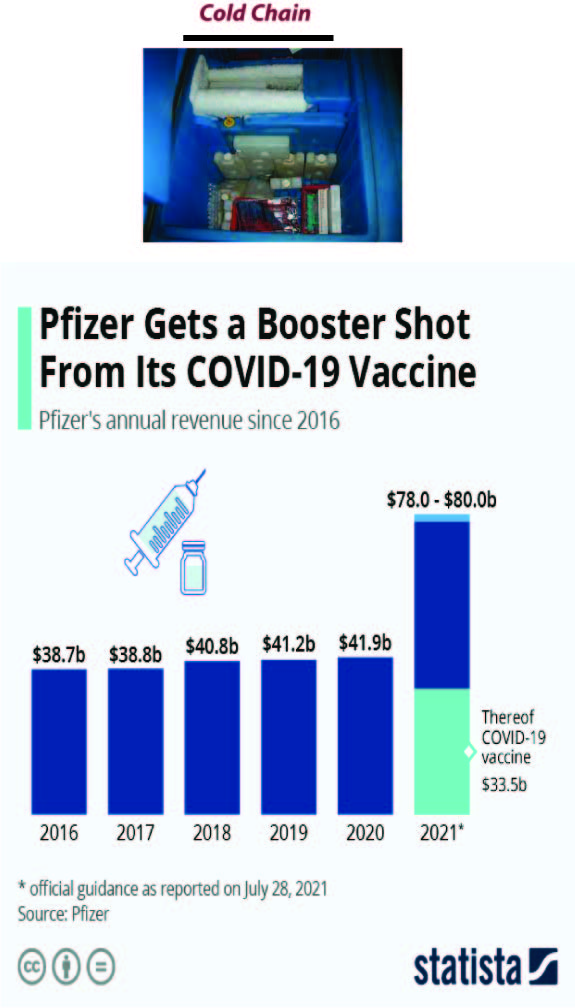
How to Explain Cold Chain as a Supply Chain and Logistical issue? |
- ikram
- March 15, 2025
- 0
Trending Posts
View AllWhat Are Box Logistics, Containerization, Ports In A Global Shipping Network? |
- ikram
- August 10, 2025
- 3
Containers are the primary mode of transportation for maritime import and export flows, with 75%…
How Does Semiconductor Technology Impact the Global Supply Chain?
- ikram
- June 21, 2025
- 0
The industry`s annual semiconductor sales revenue has since grown to over $481 billion, as of…
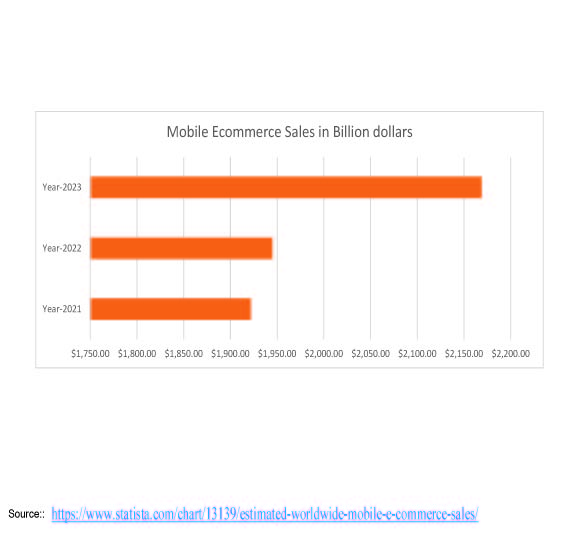
How to explain the rise of ecommerce challenges and opportunities for supply chain management?
- ikram
- July 21, 2025
- 0
The rise of e-commerce has brought significant changes to the global economy, altering industries and…
How to enhance supply chain management efficiency using AI technology? |
- ikram
- July 3, 2025
- 0
AI uses historical sales, market trends, weather, and social media to predict demand with higher…
Latest Posts
View AllWhat Are Box Logistics, Containerization, Ports In A Global Shipping Network? |
- ikram
- August 10, 2025
- 3
Containers are the primary mode of transportation for maritime import and export flows, with 75% of total cargo carried by containers in developed areas of a global shipping network. Containerization…
How Does Semiconductor Technology Impact the Global Supply Chain?
- ikram
- June 21, 2025
- 0
The industry`s annual semiconductor sales revenue has since grown to over $481 billion, as of 2018. In 2021, the sales of semiconductors reached a record $555.9 billion, up 26.2 percent…
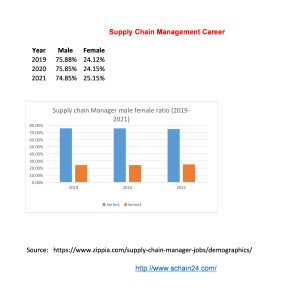
What is a Supply Chain Management Job and Career?
- ikram
- January 27, 2025
- 0
In a case study, based on US-based companies, first-level management is of about 0-4 years. To understand the supply chain management job and career we can remind ourselves about the…
What is the Role of Inventory in Supply Chain Management?
- ikram
- January 13, 2025
- 0
In Supply Chain Management (SCM), efficient inventory management is the result of a combination of interdependent procedures that work together to promote robustness and efficiency. Making wise decisions is necessary…
What Makes Toyota’s Supply Chain Management a Benchmark for Excellence?
- ikram
- January 2, 2025
- 0
Toyota has an effective supply chain strategy that puts value and efficiency first. It has adopted the Just-In-Time (JIT) system, which guarantees on-demand delivery of materials and components while cutting…
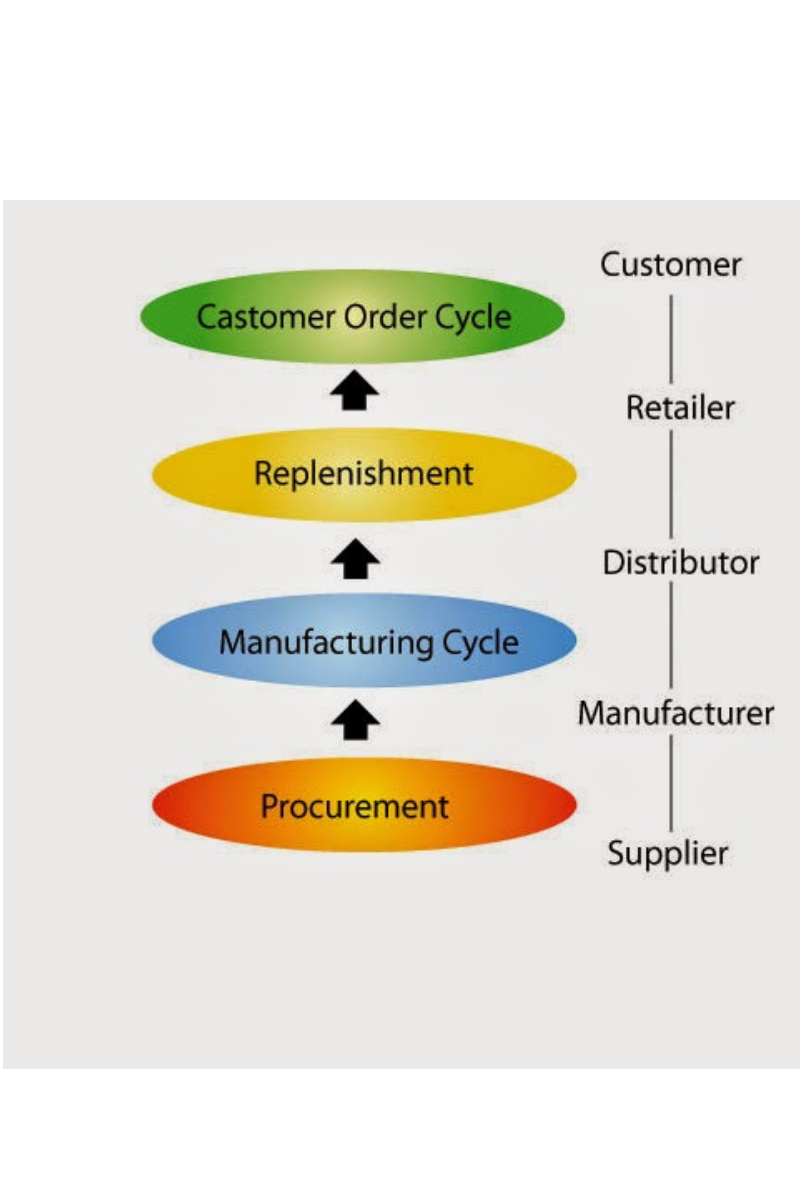
What is Cycle View of a Supply Chain? Is it Useful? |
- ikram
- December 12, 2024
- 6
The processes in a Supply Chain are usually divided into a series of cycles, each performed in the interface between two interrelated successive stages of a Supply Chain. Sub-processes in…
Supply Chain Management
View AllWhat Are Box Logistics, Containerization, Ports In A Global Shipping Network? |
- ikram
- August 10, 2025
- 3
Containers are the primary mode of transportation for maritime import and export flows, with 75% of total cargo carried by…
How Does Semiconductor Technology Impact the Global Supply Chain?
- ikram
- June 21, 2025
- 0
The industry`s annual semiconductor sales revenue has since grown to over $481 billion, as of 2018. In 2021, the sales…
What is Cycle View of a Supply Chain? Is it Useful? |
- ikram
- December 12, 2024
- 6
What Are Box Logistics, Containerization, Ports In A Global Shipping Network? |
- ikram
- August 10, 2025
- 3
Abstract Containers are the primary mode of transportation for maritime import and export flows, with 75% of total cargo carried by containers in developed areas of a global shipping network.…
How Does Semiconductor Technology Impact the Global Supply Chain?
- ikram
- June 21, 2025
- 0
Abstract The industry's annual semiconductor sales revenue has since grown to over $481 billion, as of 2018. In 2021, the sales of semiconductors reached a record $555.9 billion, up 26.2…
How to explain the rise of ecommerce challenges and opportunities for supply chain management?
- ikram
- July 21, 2025
- 0
Abstract The rise of e-commerce has brought significant changes to the global economy, altering industries and consumer behavior. However, it has also presented challenges and opportunities for supply chain management.…
How to enhance supply chain management efficiency using AI technology? |
- ikram
- July 3, 2025
- 0
Abstract AI uses historical sales, market trends, weather, and social media to predict demand with higher accuracy so that it enhances supply chain management efficiency. Machine learning models detect patterns…
What Are Box Logistics, Containerization, Ports In A Global Shipping Network? |
- ikram
- August 10, 2025
- 3
Containers are the primary mode of transportation for maritime import and export flows, with 75% of total cargo carried by containers in developed areas of a global shipping network. Containerization…
How Does Semiconductor Technology Impact the Global Supply Chain?
- ikram
- June 21, 2025
- 0
The industry`s annual semiconductor sales revenue has since grown to over $481 billion, as of 2018. In 2021, the sales of semiconductors reached a record $555.9 billion, up 26.2 percent…
What is Cycle View of a Supply Chain? Is it Useful? |
- ikram
- December 12, 2024
- 6
The processes in a Supply Chain are usually divided into a series of cycles, each performed in the interface between two interrelated successive stages of a Supply Chain. Sub-processes in…
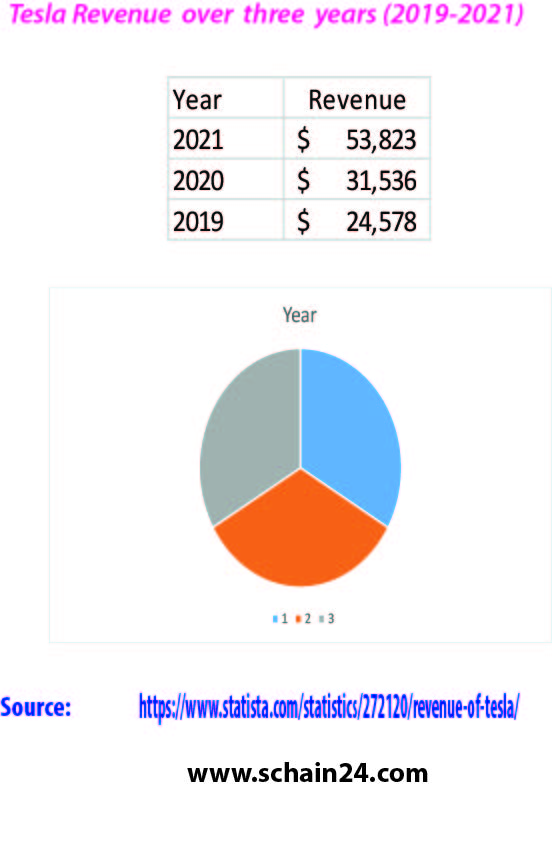
Tesla’s supply chain and logistics: A case study
- ikram
- May 1, 2023
- 0
The company was incorporated as Tesla Motors, Inc. on July 1, 2003, by Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning. Eberhard verbalized he wanted to build a car manufacturer that is additionally…
H & M Supply Chain management: A case study
- ikram
- January 8, 2023
- 0
Hennes & Mauritz AB is a Swedish multinational clothing-retail company known for its fast-fashion clothing for men, women, teenagers, and children. As of November 2019, H&M operates in 74 countries…
What Makes Toyota’s Supply Chain Management a Benchmark for Excellence?
- ikram
- January 2, 2025
- 0
Toyota has an effective supply chain strategy that puts value and efficiency first. It has adopted the Just-In-Time (JIT) system, which guarantees on-demand delivery of materials and components while cutting…
Trending
View AllEditor’s Picks
View All
Follow Us On
Popular Posts
View AllRecent
View AllWhat Are Box Logistics, Containerization, Ports In A Global Shipping Network? |
- ikram
- August 10, 2025
- 3
Containers are the primary mode of transportation for maritime import and export flows, with 75%…
How Does Semiconductor Technology Impact the Global Supply Chain?
- ikram
- June 21, 2025
- 0
The industry`s annual semiconductor sales revenue has since grown to over $481 billion, as of…
How to explain the rise of ecommerce challenges and opportunities for supply chain management?
- ikram
- July 21, 2025
- 0
The rise of e-commerce has brought significant changes to the global economy, altering industries and…
How to enhance supply chain management efficiency using AI technology? |
- ikram
- July 3, 2025
- 0
AI uses historical sales, market trends, weather, and social media to predict demand with higher…