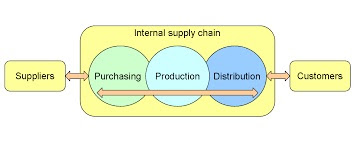
Abstract Supplier Scoring is used to rate Supplier performance.Impact on Supply Chain surplus and total cost is the basis of comparison between suppliers.If sourcing process is effective it improves profits for the firm and total supply chain in various ways. A firm may like to keep a supply chain function in the house if outsourcing increases the third party power significantly. Firms often like to keep the supply chain function in the house, if there is a chance to leakage of intellectual property or other sensitive information, especially when the third party also serves the competitors also.Since late 1990s the trend of outsourcing a greater range of supply chain function has been growing.With more globalization of business customers are looking for players, who can manage virtually all aspects of their Supply Chain, which is being called 4PL.A 4PL is an integrator ,who assembles the supply chain resources, capability and technical areas of its own and other organization to design, build and run comprehensive supply chain solutions. Keywords:Sourcing Decisions and Third Party Supply Chain Management Introduction Sourcing is the whole set of business processes, which is necessary to buy goods and services required by the Supply Chain. Most important decision for a supply chain function is whether it is feasible to outsource or perform the function in- house. When […]
Search Results for: supply chain planning
A discussion about the Value Chain (VC) concept and Business strategy
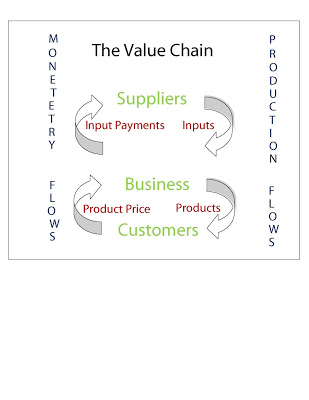
Abstract A firm value chain is a representation of various processes involved in producing goods and services starting with raw materials and ending with delivery of the finished goods to the customer.Value chain begins with new product development, which creates new product or service.The functioning of the value chain is supported by the human resources, accounting and Information technology.The value […]
Bonded Warehouse and Supply Chain Management issues(Part-1):
Supply Chain Management (SCM) involves designing, planning, executing, controlling, and monitoring supply chain activities to increase value, build infrastructure, leverage logistical needs, supply and demand, and measure performance globally. SCM integrates with logistics, procurement, operations management, and information technology. Bonded warehouses are secure areas where dutiable goods are stored without duty payment, managed by the state or private companies. Special Economic Zones (SEZs) are bonded logistical parks with trade arrangements over specific geographic areas, under customs supervision, and integral to the global supply chain.
A discussion to eradicate misconceptions about Green Supply Chain Management (GSCM)
Abstract GSCM aims to minimize or eliminate wastages including hazardous chemicals, emissions, energy, and solid waste along the supply chain such as product design, material resourcing, manufacturing process, and distribution of final product management business activities can pose a paramount threat to the environment in terms of carbon monoxide emissions, discarded packaging materials, scrapped toxic materials, traffic congestion and other […]
Supply Chain education & certification: Highlights on curriculum and other related issues :
Introduction: ISCEA is the world leader in Supply Chain education , certification & different recognition programs e.g. Certified Supply Chain Manager(CSCM), Certified Supply Chain Analyst(CSCA),Post graduate diploma in Supply Chain Management (PGDSCM) etc. In this blog article will discuss about CSCM, CSCA & PGDSCM so that those who are interested in Supply Chain Education and certification will get some important […]
IMAFS The Inventory Optimization Software
Abstract IMAFS the inventory optimization software helps knowledge gathering areas, such as, solution oriented and stock availability management, best practices in inventory management, support from experts, evolution of ROI before implementation and simplify integration, proven and rigorous implementation methodology using cloud/SAAS mode, continuous improvement with R&D, and user-friendly, integration manual parameters also. A poor delivery performance can affect consumption history.A […]
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): Its Effects On Businesses and Brands |
Achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) is a critical role for businesses and brands, as it can have a big impact on their operations, strategies, branding, and stakeholder interactions. In order to meet global sustainability goals, promote innovation in goods and services as well as business models, and draw in socially conscious clientele, companies are incorporating the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) into their plans. ESG factors are also being considered by investors when making decisions, and businesses that support the SDGs stand to gain access to sustainable finance sources and a greater number of investments.
Goals such as “Climate Action” and “Responsible Consumption and Production” can encourage companies to streamline their supply chains, cut waste, and use more environmentally friendly production techniques. Governments are putting SDG-aligned laws into effect, and businesses need to follow them to avoid fines or reputational harm.