Abstract
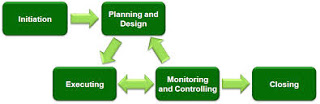
To serve the customer, Supply Chain Management (SCM) needs to design, plan, execute, control, and monitor Supply Chain activities. Their objective is to create and increase the value of the Supply Chain, build the necessary infrastructure, leverage logistical needs, supply, and demand, and measure performance even at the global level. It’s more accurate to use the term “Supply network” or “Supply web”. Supply chain profitability is the total profit to be shared across all stages of the supply chain. Supply chain success should be measured by total supply chain profitability, not profits at an individual stage. Sources of supply chain cost are flows of information, products, or funds between stages of the supply chain. Supply chain management is the management of flows between and among supply chain stages to maximize total supply chain profitability.
Keywords: Supply Chain Management (SCM), supply chain profitability, Customers, etc.
Introduction
As Customers are at the end of the network and need certain products or services, Supply Chain Management is the management of networks and channels involved that serve the customer. SCM covers the movement and storage of raw materials, WIP, and finished goods from point of start to point using the finished goods or services. There are different parties involved in a Supply Chain such as manufacturers, marketers, suppliers, transporters, warehouses, retailers, customers, etc. They are directly or indirectly involved in the fulfillment of customer requirements. The main objective is to maximize the overall value generated. They continually look for sources of revenue and cost.
An integrated approach
To serve the customer, Supply Chain Management needs to design, plan, execute, control, and monitor Supply Chain activities. And their objective is to create and increase the value of the Supply Chain, build the necessary infrastructure, leverage logistical needs, supply, and demand, and measure performance even at the global level. SCM tends to be an integrated approach along with logistics, procurement, operations management, and information technology.
SCM Components
SCM comprises all Stages involved, directly or indirectly, in fulfilling a customer request including manufacturers, suppliers, transporters, warehouses, retailers, and customers. Within each company, the supply chain includes all functions involved in fulfilling a customer request (product development, marketing, operations, distribution, finance, and customer service). The Customer is an integral part of the Supply Chain.
A Network
SCM includes the movement of products from suppliers to manufacturers to distributors. It also includes the movement of information, funds, and products in both directions. It’s more accurate to use the term “supply network” or “supply web”. The network involves all firms and relationships that get a product to market, including the original acquisition of raw materials; production of the item at a manufacturing facility; distribution to a retailer; sale of the finished item to the customer, and any installation, repair, or service activities that follow the sale.
Typical Supply Chain stages
It includes Customers, retailers, distributors, manufacturers, and suppliers. All stages may not be included in all the supply chains. Supply chain management discusses inputs, conversion, and outputs, while purchasing, deals with purchased goods, materials, and services supply chain management discusses inputs, conversion, and outputs.
Supply Chain profit
The objective of every Supply Chain is to maximize the overall value generated. Value is the difference between what the final product is worth to the customer and the costs the supply chain incurs in filling the customer’s request. Value is strongly correlated with supply chain profitability (also known as supply chain surplus). Supply chain profitability is the total profit to be shared across all stages of the supply chain.
Supply Chain Cost
Supply chain success should be measured by total supply chain profitability, not profits at an individual stage. The sources of supply chain revenue are the customer. Sources of supply chain cost are flows of information, products, or funds between stages of the supply chain. Supply chain management is the management of flows between and among supply chain stages to maximize total supply chain profitability.
Example of a supply chain
For easy understanding, we may cite an example of US Textile & Apparel Supply Chain about 25,000 companies are working, where about 50,000 people are involved excluding retailing channels, which has five segments. At the top of the Supply Chain, there are fiber producers. In the second segment, fibers are spun, woven, or knitted, which are usually called textile mills. The Third segment of the supply chain is apparel manufacturers or other textile products manufacturers. The fourth segment is the retailers who make the products available to customers. Then, the customer is the final part of the supply chain. All the earlier four segments are working to satisfy the customer’s needs.
Conclusion
As Customers are at the cessation of the network and need certain products or accommodations, Supply Chain Management is the management of networks and channels involved that accommodate the customer. SCM covers the kineticism and storage of raw materials, WIP, and finished goods from point of start to point of utilizing the finished goods or services. To accommodate the customer, Supply Chain Management needs to design, plan, execute, control, and monitor Supply Chain activities. SCM comprises of all Stages involved, directly or indirectly, in consummating a customer request including manufacturers, suppliers, conveyors, warehouses, retailers, and customers. Within each company, the supply chain includes all functions involved in consummating a customer request. Balancing between effectiveness and responsiveness, and building a greener supply chain, are among the long-term and short-term goals of a Supply Chain.
Further readings:
1. Walker.Helen, Sisto.Lucio D.,Mc Bain,Danan(2008). “Drivers and barriers to environmental supply chain management practices: Lessons from the public and private sectors”. Journal of Purchasing and Supply Management. Volume 14, Issue 1, March 2008, Pages 69-85
2. Diabat.Ali, Govindan.Kannan(2011). “An analysis of the drivers affecting the implementation of green supply chain management.Resources, Conservation and Recycling”, Volume 55, Issue 6, April 2011, Pages 659-667
3.https://youtube.com/shorts/nIJpfKu4dg8?feature=share
4.https://youtu.be/6GGH6INaRe4?si=ynvHgjTrypc9pnAN
5.https://rumble.com/v3oqo2b-how-can-supply-chain-management-help-your-business-succeed.html