Abstract The logistical drivers are facilities, inventory, and transportation. Inventory denotes all raw materials, WIP, and finished goods in a supply chain. On the other hand, transportation involves moving inventory from point to point. Information is data about facilities, inventory, transportation, costs, prices and customers throughout the supply chain, also gives shipping options to managers. Pricing drivers determine the price […]
Search Results for: supply chain planning
A brief discussion about digital supply chain management
Digital supply chain risk due to the potential for Internet of Things (IoT) security vulnerabilities, which arise when assets and machines share data via sensors and software, the digital supply chain may be exposed to danger. Stages of digital supply chain management involve planning out processes and inventory before advancing to order management.
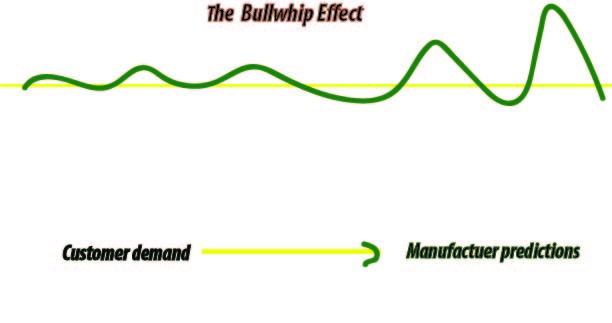
A discussion about lack of supply chain coordination and the bullwhip effect
In SCM, a supply chain manager coordinates the logistics of all the aspects of the supply chain which consists of five parts: the plan or strategy, the source of raw materials and services, manufacturing, i.e., productivity and efficiency, delivery and logistics, the return system for defective and unwanted goods etc. The phenomenon that fluctuation in orders increases as one moves up the supply chain from retailers to wholesalers to manufacturers to suppliers is referred to the bullwhip effect. Managers can help achieve coordination in supply chain by aligning goals and incentives across different functions and stages of the supply chain. When supply chain moves from retailers to wholesalers to manufacturers to suppliers, the bullwhip effect occurs. It results in different stages optimizing local objectives instead of total supply chain profits. The bullwhip effect results in costs in the supply chain and decrease in levels of customer service.
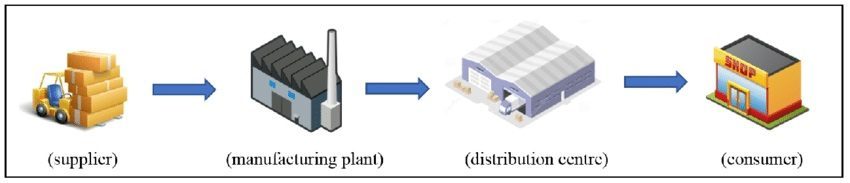
Supply chain: how to define the term and the process in general
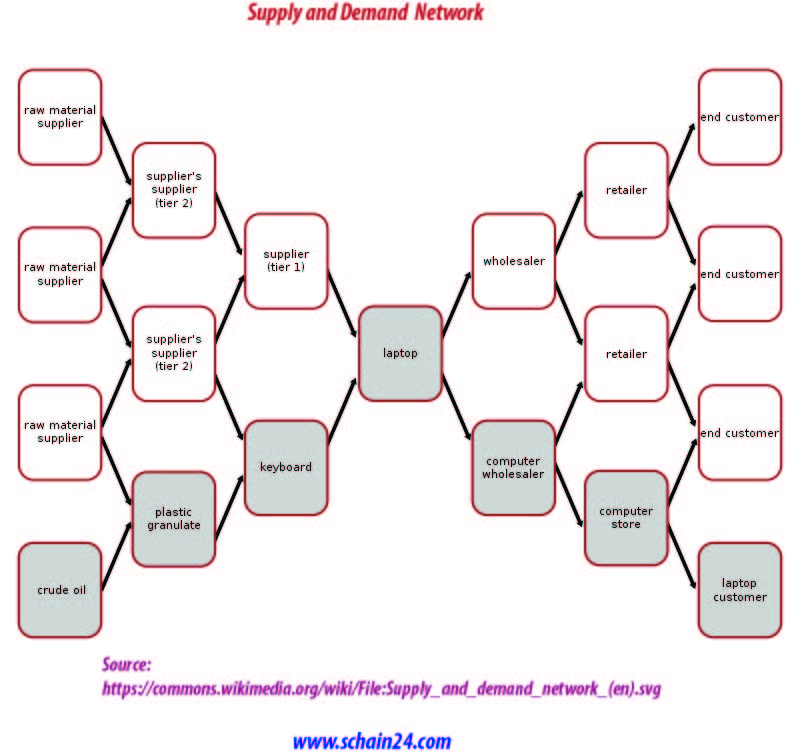
The design decisions determine the supply chain configuration and set constraints within which other supply chain drivers can be used either to decrease supply chain cost or to increase responsiveness. Mapping your supply chain denotes accumulating information about your suppliers, their own suppliers, and the people who work in your supply chain to engender an ecumenical map of your supply network. Supply-chain-management software (SCMS) is the software tools or modules used in executing supply chain transactions, managing supplier relationships and controlling associated business processes.
What are the Roles of Network Design in the Supply Chain Management?
Though there is inherent uncertainty about the future, a supply chain network risk analysis can be conducted; by using information available, the future business environment can be characterized. Network design decisions have a significant impact on performance of the supply chain. Though designing a supply-chain network can cut costs within a company, it is important to note the supply chain is not static but rather a continually improving model and adapt in response. The allocation of supply sources and markets to facilities has a significant impact on performance because it affects total production, inventory and transportation costs incurred by the supply chain to gratify customer demand. Good network design decisions increase supply chain profits, whereas poor network design hurts profit.
A short discussion about Inbound logistics in a supply chain management perspective
Inbound logistics is related with supply chain planning. It can be easily completed if used some help of technology. A good deal of knowledge about customs and business security is also required.
Covid-19 : Her affects on global economy and supply chain
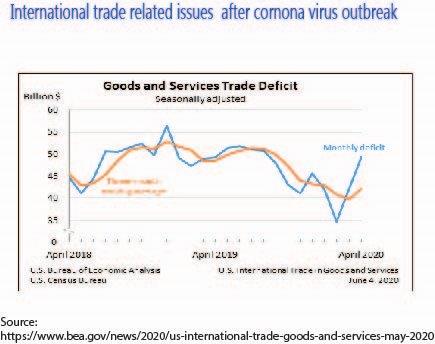
Society, businesses and governments can all be remodeled in the aftermath of the coronavirus happening, and that we hope, towards a lot of sustainable society, thus, students and managers ought to plan to think about this transformation through a positive lens so as to boost supply chains to produce high worth and even a lot of outstanding services to society, since it’s currently extravagantly clear that supply chains are the veins of the whole economy. In line with UNEC for Latin America estimate, the pandemic-induced recession might leave 14–22 million of individuals in extreme economic condition in Latin America than the scenario while not the pandemic. Lloyd’s of London has calculated that the worldwide insurance trade has to absorb losses of US$204 billion, more extraordinary than the losses from the 2017 Atlantic cyclone season and 9/11, suggesting the COVID-19 pandemic is possibly costliest disaster ever in human history. Governments are possibly to take a position and regulate “key supply chains”, like pharmaceutical, personnel protecting instrumentation and agro-food chains so as to make sure national food security. As of 6 July 2020, over 11.4 million cases of COVID-19 are reported in addition for 188 countries and territories, leading to over 533,000 deaths. On a daily basis a lot of cases are reported, and new countries enter the World Health Organization’s (WHO) list of areas wherever the virus has been reported suggested preventive measures embrace hand washing, covering one’s mouth once coughing, maintaining distance from others, sporting a mask at public settings, and observation and self-isolation for people that suspect they’re infected. The COVID-19 pandemic, referred to as the coronavirus pandemic, is in progress as the global pandemic of coronavirus illness 2019 (COVID 19), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus as a pair of (SARS CoV 2).
Keywords: covid-19, global supply chain, supply chain sustainability, economy.